V-Ball Valves VS Trunnion Ball Valves
A V-ball valve is appropriate for flow control and a trunnio ball valve is a block valve.
A trunnion ball valve (or floating for that matter) is an on/off or "block" type device. The valve position vs. allowed flow graph is very non-linear and it will allow 100% of flow at somewhere around 20-40% open. These valves should never be used by a designer in a flow-control scenario (sometimes the field guys find themselves in a situation where the only valve available for flow control is a ball valve for a one-off requirement, but the designer shouldn't ever put in a ball valve specifically for flow control).
A V-Ball valve (together with globe valves and chokes valves) are appropriate for flow control. These all have valve position vs. allowed flow graphs that approach linear.
1. Structural Design & Working Principle
- V-Ball Valve:
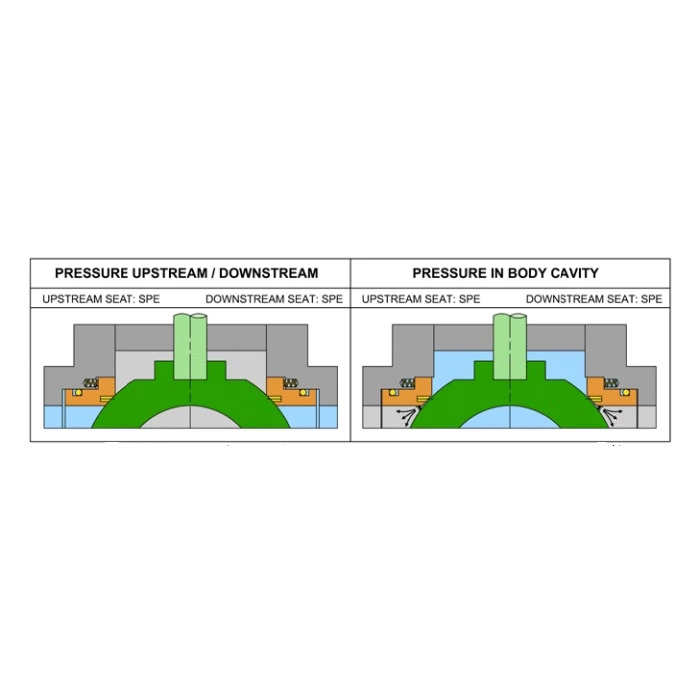
Features a V-shaped notch in the ball for precise flow control. The ball rotates to gradually expose or cover the V-port, enabling linear flow regulation. Typically uses a floating ball design (ball moves axially under pressure to seal against the downstream seat) or elastic ball design (with an internal elastic groove for high-pressure sealing) . - Trunnion Ball Valve:
Employs a fixed ball anchored by upper/lower support shafts (trunnions). The valve seats move under pressure to seal against the stationary ball. Includes anti-blowout stem designs (e.g., stepped shaft with shoulder and graphite-PTFE backup rings) to prevent stem ejection under high pressure .
2. Flow Characteristics & Control Precision
| Feature | V-Ball Valve | Trunnion Ball Valve |
|---|---|---|
| Flow Regulation | Superior (linear flow characteristic via V-notch) | Limited (primarily for on/off) |
| Flow Capacity | Reduced (Kv ~0.5 due to V-port) | Full-bore (Kv ~1; minimal pressure drop) |
| Shearing Action | Cuts fibers/slurries during rotation | Not applicable |
3. Pressure & Torque Performance
- V-Ball Valve:
- Suitable for low-to-medium pressure (floating ball design).
- Higher operating torque due to shearing action in slurries .
- Trunnion Ball Valve:
- Optimized for high pressure (Class 600+ per API 6D).
- Bearings reduce torque by 40% vs. floating designs.
- Anti-blowout stems withstand 4× rated pressure (API 607) .
4. Sealing Mechanisms
| Aspect | V-Ball Valve | Trunnion Ball Valve |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Seal | Single downstream seat (soft materials like PTFE) | Dual piston-effect seats (metal/PTFE) |
| Fire Safety | Limited | Fire-safe metal backup seals (30+ mins) |
| DBB Function | No | Yes (Double Block & Bleed via body vent) |
5. Applications
- V-Ball Valve:
Ideal for throttling viscous/pulp media (e.g., paper pulp, sewage, powders) where precise control is critical. - Trunnion Ball Valve:
Dominates high-pressure isolation (e.g., oil/gas pipelines, hydrogen systems):- Handles 70MPa hydrogen with metal/graphite seals.
- Chlorine service with PTFE-lined bodies and bellows stems.
- Cryogenic variants (-196°C) .
6. Standards & Certifications
- V-Ball: Focus on control standards (e.g., IEC 60534 for industrial automation).
- Trunnion: Complies with API 6D/607, ASME B16.34 (pressure testing at 150% rating), and IEC 62271 (gas insulation systems) .